Mitral Valve Anatomy and Function
Table of Contents
It is essential to have a good understanding of mitral valve anatomy to comprehend its function and the impact of different heart conditions. The mitral valve plays a vital role in controlling the flow of blood between the left atrium and left ventricle, making it a crucial part of the heart’s structure. This article will delve into the detailed anatomy of the mitral valve, covering its structure, function, and clinical importance.
What is Mitral Valve
Situated on the left side of the heart, the mitral valve, also called the bicuspid valve, is positioned between the left atrium and left ventricle. Mitral Valve Anatomy shows that it contains two leaflets that prevent blood from flowing backward during heart contractions. This component is essential for maintaining the heart’s proper blood flow and pressure, thereby ensuring efficient circulation throughout the body.
Function
Before understanding the mitral valve anatomy, it is crucial to comprehend the route that blood takes as it flows through the mitral valve in order to understand its purpose.
When the atrium contracts, it propels blood through the open mitral valve into the left ventricle. This action enables the left ventricle to be filled with blood while the valve stays open. When the ventricle contracts, it pumps blood into the aorta, leading to the closure of the mitral valve and preventing any reverse flow into the atrium.Understanding this sequence is crucial for grasping Mitral Valve Anatomy and its role in maintaining effective blood circulation throughout the body.
Maintaining Blood Flow:
- During the relaxation phase of the heart, known as diastole, the mitral valve opens to let oxygen-rich blood from the lungs fill the left atrium, and then flow into the left ventricle.
- When the left ventricle is filled, the mitral valve shuts as the heart squeezes. This action stops blood from returning to the atrium, guaranteeing that all the blood is effectively pumped into the aorta and circulated throughout the body.
Maintaining Pressure:
- When closed, the mitral valve maintains a seal to regulate pressure in the heart. Effective blood pumping relies on proper pressure, so a leak in the valve could cause inefficient pumping and an increase in pressure in the atrium.
Decoding Mitral valve Anatomy
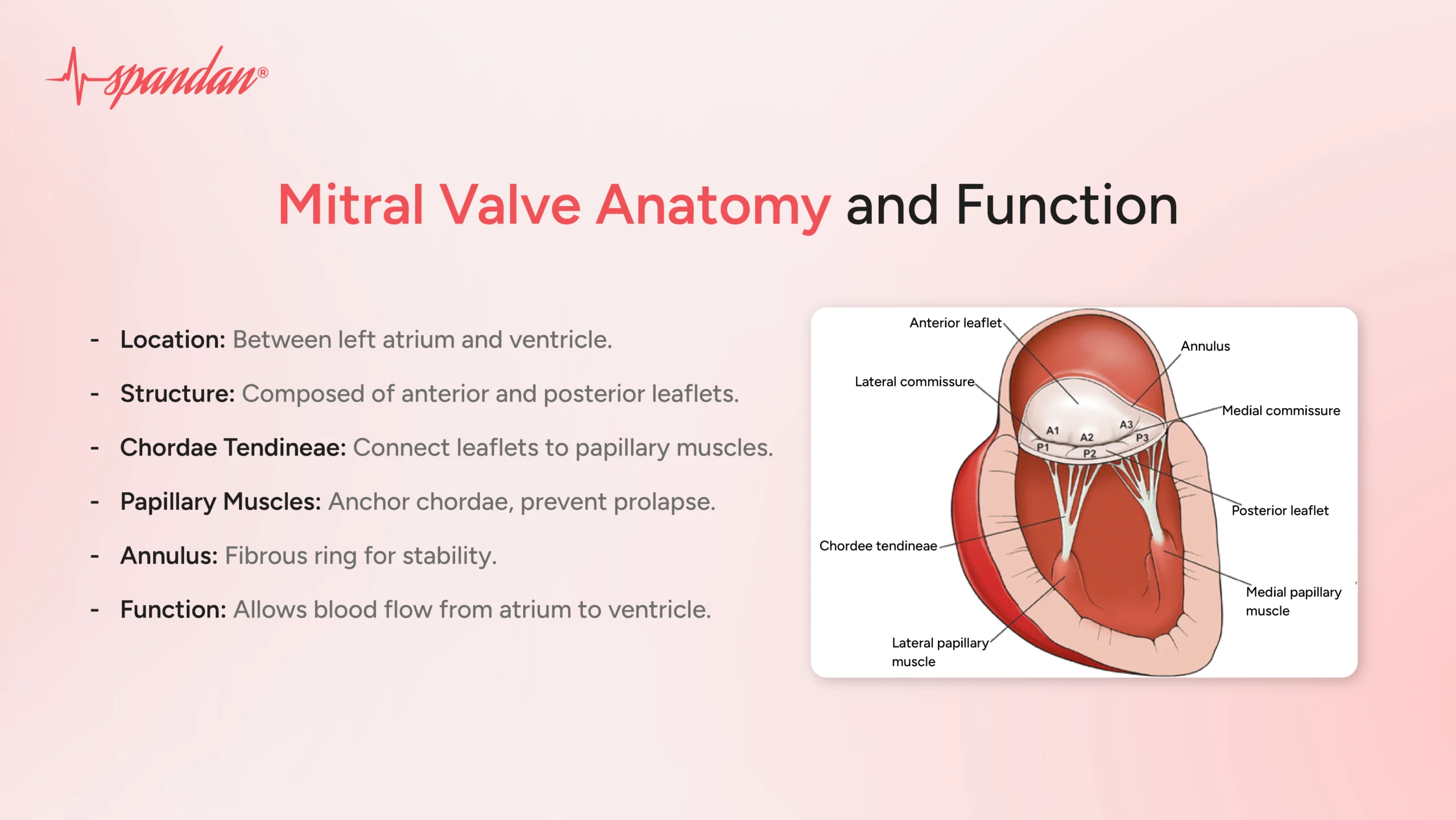
Leaflets: The mitral valve is made up of two main leaflets:
- Anterior Leaflet: The anterior leaflet exceeds the posterior leaflet in size, thickness, and length. This greater size enables it to effectively handle the elevated pressures in the left ventricle during contraction. Playing a vital role, the anterior leaflet maintains a strong seal to prevent the backflow of blood into the left atrium when the ventricle contracts.
- Posterior Leaflet:The posterior leaflet is smaller and thinner in comparison to the anterior leaflet, which enables it to be flexible and adaptable while the valve is opening and closing.
Chordae Tendineae: The chordae tendineae consist of slender, fibrous strands linking the mitral valve leaflets to the papillary muscles located inside the ventricle. Their function is crucial in preserving the valve’s alignment and preventing prolapse, which is the inward bulging, when the ventricle contracts.
Papillary Muscles: The walls of the left ventricle give rise to papillary muscles, which are connected to the chordae tendineae. These muscles contract at the same time as the ventricle, which assists in stabilizing the leaflets and ensuring that the mitral valve stays shut during ventricular systole.
Annulus: The base of the valve is formed by the fibrous ring known as the mitral valve annulus, which offers structural support and preserves the valve’s shape. During the cardiac cycle, the annulus is capable of changing in size and shape, enabling the valve to adjust to varying blood volumes.
Fibrous continuity: The fibrous tissue called the aortic-mitral curtain connects the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve to the aortic valve, offering structural support and preserving the anatomical connection between the two valves. This continuity is essential for maintaining proper function and stability throughout the cardiac cycle, facilitating efficient blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta and preventing any interference between the valves.
Interstitial cells: The maintenance of the mechanical and metabolic balance of the heart valves relies heavily on the interstitial cells, which are situated within the valve structure. These cells help uphold the integrity of the extracellular matrix, thereby preserving the flexibility and strength of the valves.
Endothelial cells: The communication between endothelial cells and interstitial cells is essential for maintaining the shape and strength of heart valves.
Mitral Valve Disorders
The function of the mitral valve can be affected by several conditions, which can result in different clinical implications.
- Mitral Regurgitation:During ventricular contraction, this condition occurs due to the improper closure of the mitral valve, which results in blood flowing back into the left atrium. The backflow of blood can lead to symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and palpitations by increasing the atrial blood volume. If left untreated, mitral regurgitation can cause the heart to work harder, potentially resulting in the enlargement of the left atrium and heart failure over time.
- Mitral Stenosis:The mitral valve becomes narrowed in this condition, limiting the flow of blood from the left atrium to the left ventricle. Rheumatic fever or other factors can cause this constriction, leading to increased pressures in the left atrium. Common symptoms include breathlessness, particularly during physical activity, tiredness, and swelling in the legs caused by retained fluid.
- Mitral Valve Prolapse: The abnormal bulging of the mitral valve leaflets into the left atrium during contraction characterizes this condition. Although many individuals with mitral valve prolapse do not experience any symptoms, they can still lead normal lives.
In summary, effective blood circulation relies heavily on the proper operation of the mitral valve, and understanding Mitral Valve Anatomy is a handy practice for medical students and clinicians alike. Recognizing the order of blood movement during atrial and ventricular contractions underscores the significance of mitral valve anatomy in sustaining this function. The structural soundness and function of the mitral valve guarantee efficient blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle, underscoring the crucial role of mitral valve anatomy in maintaining overall heart health.