Author:- Mr. Ritesh Sharma
An electrocardiogram is one of the most important tests in the field of cardiac care. Whenever someone faces a heart-related symptom, this test is performed by healthcare professionals. Now, due to this, knowing the 12 Lead ECG Placement completely is of utmost importance. If the 12 Lead ECG Placement is not correct, the electrical activity of the heart from different parts of the body will not be captured accurately. Moreover, the people who are aspiring healthcare professionals need to learn the 12 Lead ECG Placement for correct patient care in their career.
In this blog, we will provide you with the complete guide for the 12 Lead ECG placement. Therefore, the next time you perform a 12-lead ECG test, you get confident enough to place all leads on the skin at the right positions. This guide offers a detailed look at the placement of each lead, ensuring precise and reliable results.
Understanding the 12-lead Electrocardiogram
Before delving into 12 Lead ECG placement, we shall learn, what a 12-lead ECG entails. A 12-lead ECG provides a comprehensive view of the heart’s electrical activity from multiple angles. It includes three limb leads, three augmented leads, and six precordial (chest) leads. Each lead records the heart’s electrical impulses from a specific direction, helping to diagnose various cardiac conditions.
In a 12-lead ECG, the abnormalities are diagnosed through waveform analysis. Therefore, it showcases P-wave ECG abnormalities, QRS complex abnormalities, and T-wave abnormalities in the report. If you happen to have any of these abnormalities then you might be suffering from a variety of heart conditions ranging from heart palpitations to cardiac arrhythmias to a heart attack.
12 Lead ECG Placement
Now, let’s move on to the complete guide for a 12 Lead ECG Placement. We have segregated different facets of a 12 Lead ECG Placement below.
Equipment Needed
Before starting, ensure you have the following:
- ECG machine
- Electrodes (stick-on pads)
- Conductive gel (if not pre-applied on electrodes)
- Skin preparation materials (alcohol wipes, razors for chest hair if necessary)
Patient Preparation
- Explain the Procedure: Ensure the patient understands the procedure to reduce anxiety.
- Position the Patient: Have the patient lie down comfortably on their back.
- Expose the Chest: Ensure the chest is exposed; for females, provide a gown to maintain modesty.
- Clean the Skin: Use alcohol wipes to clean the skin where the electrodes will be placed. This helps in obtaining a good electrical contact.
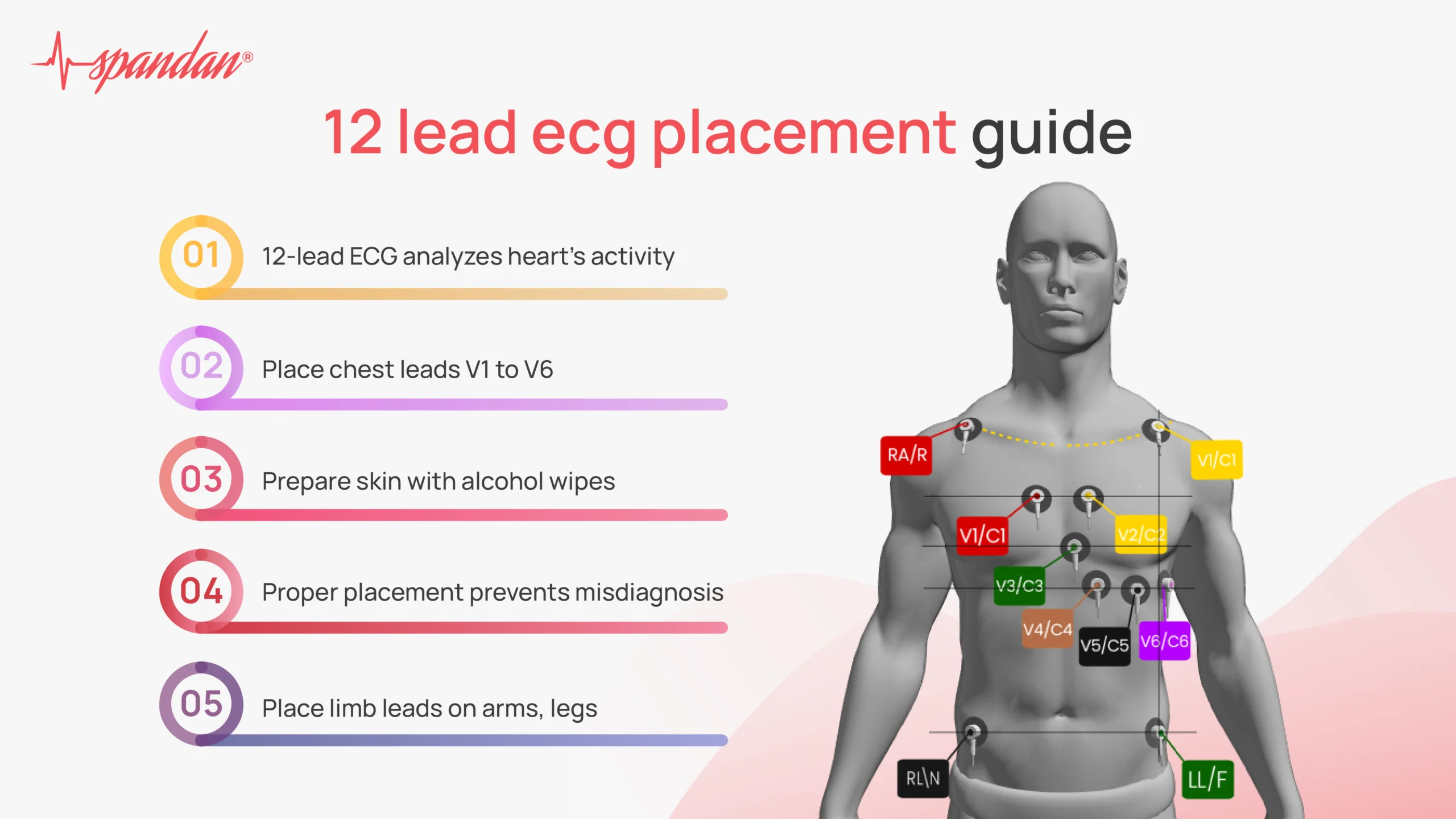
Lead Placement
The limb leads are placed on the arms and legs and include Leads I, II, III, aVR, aVL, and aVF.
- RA (Right Arm): Place an electrode on the right arm, avoiding bony areas.
- LA (Left Arm): Place an electrode on the left arm, similar to the right.
- RL (Right Leg): Place an electrode on the right leg, just above the ankle or lower leg.
- LL (Left Leg): Place an electrode on the left leg, mirroring the right leg.
Precordial (Chest) Leads
The six precordial leads (V1 to V6) provide a detailed view of the heart’s horizontal plane.
- V1: Place the electrode in the fourth intercostal space, just to the right of the sternum.
- V2: Place the electrode in the fourth intercostal space, just to the left of the sternum.
- V3: Place the electrode between V2 and V4.
- V4: Place the electrode in the fifth intercostal space at the midclavicular line.
- V5: Place the electrode horizontally even with V4, at the anterior axillary line.
- V6: Place the electrode horizontally even with V4 and V5, at the midaxillary line.
Tips for Accurate Placement
- Identify Landmarks: Use anatomical landmarks such as the sternum, clavicle, and rib spaces to accurately place electrodes.
- Consistency: Ensure leads are placed consistently in the same positions for each ECG to allow for accurate comparison over time.
- Patient Relaxation: Encourage the patient to relax and breathe normally to reduce artifacts in the ECG recording.
- Avoid Bony Areas: Place electrodes on fleshy parts of the limbs and chest to enhance signal quality.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Poor Signal Quality: Ensure good skin preparation and proper electrode adhesion. Check for dried conductive gel.
- Movement Artifacts: Ask the patient to remain still and avoid talking during the recording.
- Incorrect Lead Placement: Double-check lead positions if the ECG tracing appears abnormal.
Interpreting the 12-Lead ECG
After placing the leads and obtaining the ECG tracing, interpreting the results involves analyzing various waveforms and intervals.
- P Wave: Represents atrial depolarization.
- QRS Complex: Represents ventricular depolarization.
- T Wave: Represents ventricular repolarization.
- PR Interval: The time from the start of the P wave to the start of the QRS complex.
- ST Segment: The time from the end of the QRS complex to the start of the T wave.
- QT Interval: The time from the start of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave.
Common Findings
- Normal Sinus Rhythm: Regular rhythm with a P wave before each QRS complex.
- Atrial Fibrillation: Irregular rhythm with no distinct P waves.
- Myocardial Infarction: ST-segment elevation or depression, abnormal Q waves.
- Bundle Branch Block: Widened QRS complexes.
Importance of Proper Lead Placement
Accurate lead placement is vital for diagnosing conditions such as myocardial infarction, arrhythmias of different arrhythmia classifications, and other cardiac abnormalities. Incorrect placement can lead to misdiagnosis or missed diagnosis, impacting patient care.
In conclusion, the proper 12 Lead ECG Placement is extremely important for healthcare professionals to get the correct interpretation regarding the heart abnormalities the patient is affected by. All the aforementioned points illustrate each facet of perfect 12 Lead ECG Placement. Every healthcare professional must keep these points in mind before performing a 12-lead ECG test on the patient.



