Author:- Mr. Ritesh Sharma
Panic Attack vs Heart Attack is a very intriguing topic in the realm of heart health. Both mirror some symptoms that lead to people believing they are facing the other medical condition. However, there are also stark contrasts between these two medical conditions that make them poles apart from each other. Let us try to elucidate it through an example. Picture this: you are sleeping at night peacefully and suddenly you start experiencing strong heart palpitations. Couple this with strong cold sweats and heavy pain in the chest as if an elephant stepped food on it.
What would be your first reaction in such a situation? You might think that you are experiencing a fatal heart attack. However, it is highly likely that what you have encountered is a fleeting panic attack which is anything but fatal. Now, the conundrum of panic attack vs heart attack gets more entangled in such a situation. It is important for you to learn the difference between the two medical conditions so that if you or your close one encounters it, you act according to the situation.
In this blog, we will explain panic attack vs heart attack in its entirety. We will give you the basic definitions of how they differ from each other, talk about their similar and contrasting symptoms, and a lot more. So, if you also get confused between panic attacks and heart attacks, don’t fret. This blog will educate you in-depth.
Panic Attack vs Heart Attack
To fully comprehend panic attack vs heart attack, let’s try to first understand their basic definitions. For this, we have segregated the meaning of a panic attack and a heart attack below.
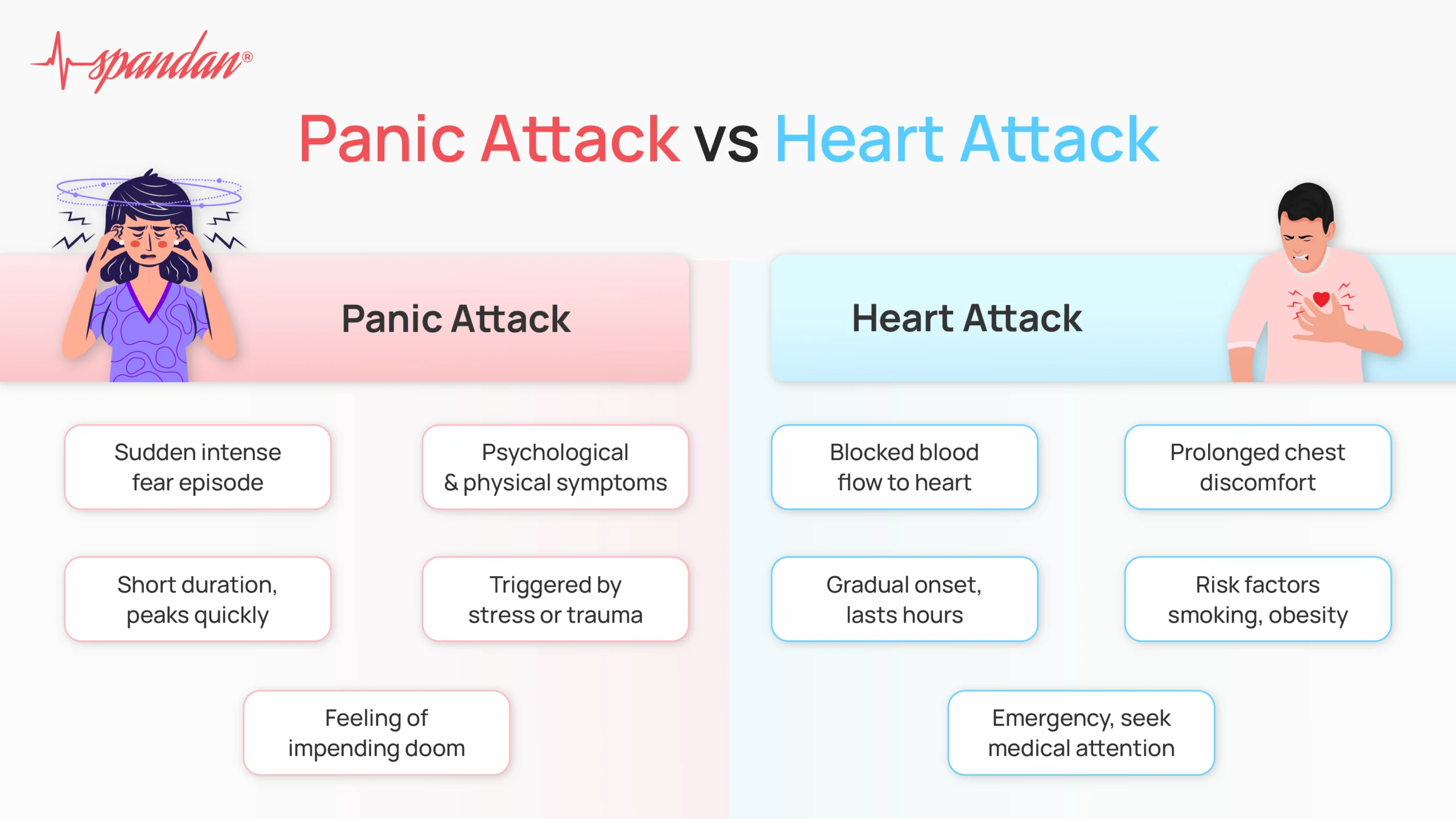
Panic Attack: A panic attack is a sudden episode of intense fear or discomfort that reaches its peak within minutes. It is characterized by a combination of physical and psychological symptoms, including rapid heart rate, chest pain, sweating, trembling, shortness of breath, dizziness, and a feeling of impending doom or loss of control. Panic attacks can occur unexpectedly or in response to specific triggers, such as stress, trauma, or phobias.
Heart Attack: A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked for a prolonged period, leading to damage or death of heart muscle cells. This blockage is often caused by the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis) in the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart. Common symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea, lightheadedness, and pain or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
The Key differences between a Panic Attack and a Heart Attack
Now, let’s delve into panic attack vs heart attack by knowing all the key differences between them one by one:
Onset and Duration:
- Panic attacks typically come on suddenly and reach their peak within minutes, often subsiding within 20 to 30 minutes. In contrast, the symptoms of a heart attack may develop more gradually over several minutes and can persist for longer periods, sometimes hours.
Physical Symptoms:
- Bo acks can cause chest pain or discomfort. However, the nature of the pain may differ. In panic attacks, chest pain is often described as sharp or stabbing and may move around the chest. On the other hand, chest pain during a heart attack is usually more prolonged and may feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or tightness, often radiating to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- Other physical symptoms, such as sweating, trembling, and shortness of breath, are common in both panic attacks and heart attacks but may vary in intensity and duration.
Psychological Symptoms:
- Panic attacks are associated with intense feelings of fear, apprehension, or impending doom, often accompanied by a sense of detachment from reality. Individuals experiencing a panic attack may fear that they are losing control, going crazy, or dying, even though there is no immediate threat to their life.
- While fear and anxiety are also present during a heart attack, they are typically secondary to the physical symptoms and the awareness of a serious medical emergency.
Triggers and Risk Factors:
- Panic attacks can occur unexpectedly or in response to specific triggers, such as stress, trauma, or phobias. They are more common in individuals with a history of anxiety disorders or other mental health conditions.
- Heart attacks are often preceded by risk factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and family history of heart disease. They can occur in individuals of any age but are more common in older adults.
Response and Treatment
When it comes to panic attack vs heart attack, the response and treatment significantly differ. While it is true that both medical conditions require prompt healthcare provider interventions, the treatment approaches in both conditions vary.
- Panic Attack: If you suspect you are having a panic attack, it’s important to try to remain calm. Practice deep breathing exercises or other relaxation techniques to help alleviate symptoms. If you have been diagnosed with panic disorder, you may have coping strategies or medications prescribed by your healthcare provider. In some cases, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can be beneficial in managing panic attacks and addressing underlying triggers.
- Heart Attack: If you or someone else is experiencing symptoms of a heart attack, call emergency services immediately. While waiting for help to arrive, it’s important to rest and avoid exertion. If you have been prescribed nitroglycerin for angina, you can take it as directed. Chewable aspirin may also help by reducing blood clotting. However, never delay calling for emergency assistance in favor of taking aspirin.
Seeking Medical Attention
Given the similarities in symptoms between panic attacks and heart attacks, it’s understandable to feel uncertain about which condition is occurring. However, it’s always better to err on the side of caution and seek medical attention if you are unsure. Healthcare professionals are trained to perform diagnostic tests, such as electrocardiograms (ECG/EKG), blood tests, and imaging studies, to determine the cause of your symptoms accurately.
ECG is an important screening test to determine whether the condition the patient is facing is a panic attack or a heart attack. While both conditions showcase an abnormal ECG, heart attacks in particular showcase t-wave abnormalities in the ECG test through ST-elevation and ST-depression.
In conclusion, the panic attack vs heart attack debate is important to understand the intricacies of the cardiovascular system and overall body. You need to differentiate between the two properly to seek the correct treatment that too promptly. That’s why it becomes paramount to take care of your heart and steer away from all kinds of troubles posed by conditions like a panic attack and a heart attack.





