Author:- Mr. Ritesh Sharma
The natural pacemaker of the heart, this term must sound familiar to you. You must have heard that our heart has a natural pacemaker that orchestrates the rhythm in the heart. The natural pacemaker of the heart plays an extremely important role in maintaining a proper rhythm of the heart while it is contracting and relaxing to complete the process of circulation. Without the origination of the rhythm from the natural pacemaker of the heart, the chambers of the heart cannot function properly to pump blood throughout the body, ensuring that all organs receive adequate amounts of oxygen and nutrients.
So, what exactly is the natural pacemaker of the heart? Moreover, how does it function to maintain the symphony of rhythm in the heart? We will delve into these questions in this blog and uncover some worthy insights. So, whether you are a clinician or a general audience, you will be educated about the natural pacemaker of the heart through this blog.
Anatomy of the Natural Pacemaker of the Heart
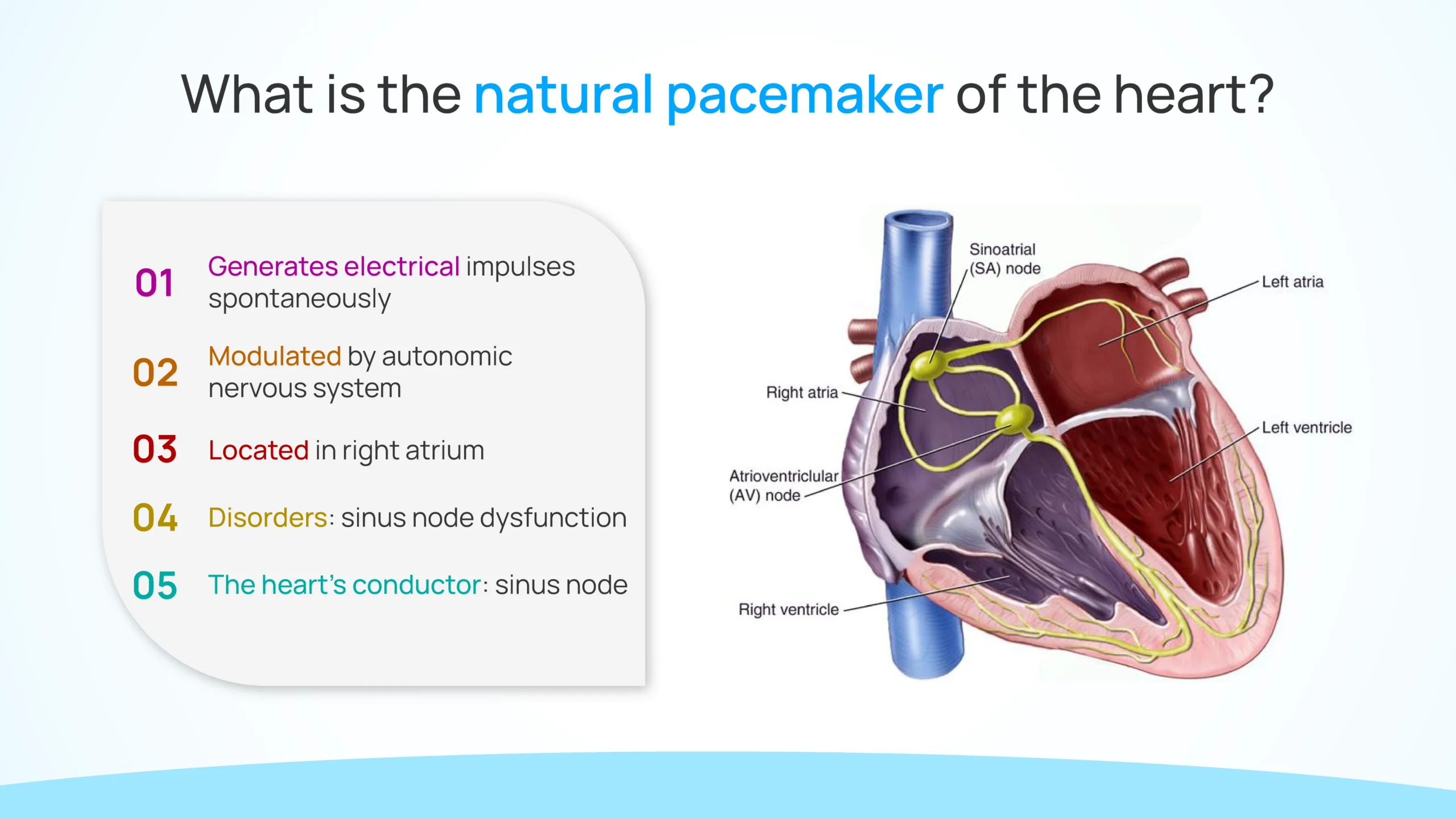
Nestled within the upper portion of the right atrium, near the junction of the superior vena cava, lies the sinus node, also known as the sinoatrial node (SAN), i.e. the natural pacemaker of the heart. Measuring only a few millimeters in size, this specialized cluster of cells serves as the primary pacemaker of the heart, generating electrical impulses that initiate each heartbeat.
Comprised of a network of specialized cells, the sinus node possesses unique properties that distinguish it from other cardiac tissues. These cells exhibit automaticity, meaning they have the inherent ability to spontaneously generate electrical impulses without external stimulation. Furthermore, the sinus node cells possess a rapid rate of depolarization, allowing them to reach the threshold for action potential initiation more quickly than surrounding cardiac cells.
Function of the Sinus Node
The primary function of the sinus node is to initiate each cardiac cycle by generating electrical impulses that propagate throughout the heart, triggering muscle contraction and subsequent pumping of blood. This process, known as cardiac conduction, ensures the coordinated contraction of the atria and ventricles, facilitating efficient blood flow through the circulatory system. Valves and septum also work along with the sinus node to ensure proper circulation. The former prevents the backflow of blood to the heart and the latter prevents the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Under normal circumstances, the sinus node serves as the dominant pacemaker of the heart, setting the pace for cardiac activity. However, in certain situations, such as during exercise or in response to hormonal fluctuations, other regions of the heart may transiently assume pacemaker function. Despite these temporary variations, the sinus node remains the primary regulator of heart rate under physiological conditions.
Modulation of Sinus Node Activity
While the sinus node generates electrical impulses spontaneously, the rate at which it does so can be modulated by various physiological and pathological factors. Autonomic nervous system input, comprised of sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation, exerts profound control over sinus node activity.
Sympathetic stimulation, mediated by the release of catecholamines such as epinephrine and norepinephrine, accelerates heart rate by increasing the rate of depolarization within the sinus node cells. Conversely, parasympathetic activity, mediated by the vagus nerve, slows heart rate by releasing acetylcholine, which inhibits the activity of the sinus node.
Additionally, circulating hormones, electrolyte concentrations, and environmental factors can influence sinus node function, contributing to dynamic variations in heart rate in response to changing physiological demands.
Disorders of Sinus Node Function
Despite its crucial role in regulating cardiac rhythm, the sinus node is susceptible to dysfunction, leading to a range of clinical conditions collectively known as sinus node dysfunction (SND). SND encompasses a spectrum of abnormalities, including cardiac arrhythmias of different arrhythmia classifications-sinus bradycardia (slow heart rate), sinus tachycardia (rapid heart rate causing heart palpitations), sinus arrest (pauses in heart rhythm), and sinoatrial exit block (impairment of electrical conduction from the sinus node).
Symptoms of SND can vary widely depending on the severity and nature of the underlying dysfunction. Common manifestations include palpitations, dizziness, syncope (fainting), fatigue, and shortness of breath. In some cases, SND may predispose individuals to more serious arrhythmias or cardiovascular complications, necessitating medical intervention.
Management of SND typically involves addressing underlying contributing factors, such as electrolyte imbalances, medication side effects, or ischemic heart disease. In cases where conservative measures are insufficient, interventions such as pacemaker implantation may be necessary to restore normal cardiac rhythm and alleviate symptoms.
The Sinus Node, Guardian of Cardiac Rhythm
In conclusion, the natural pacemaker of the heart, i.e. sinus node is the guardian of cardiac rhythm, orchestrating the symphony of the heart with remarkable precision and efficiency. Through its intrinsic electrical activity and responsiveness to regulatory inputs, the sinus node ensures the coordinated contraction of the atria and ventricles, sustaining the continuous flow of blood throughout the body.
Despite its small size, the sinus node looms large in its significance, serving as a focal point for understanding cardiac physiology and pathology. By unraveling the mysteries of this enigmatic structure, researchers and clinicians continue to advance our understanding of cardiovascular health and develop innovative strategies for diagnosing and treating cardiac rhythm disorders.
As we marvel at the intricacies of the human heart, let us not forget the humble yet extraordinary sinus node, a testament to the elegance of nature’s design and the resilience of the human spirit.



