Author:- Mr. Ritesh Sharma
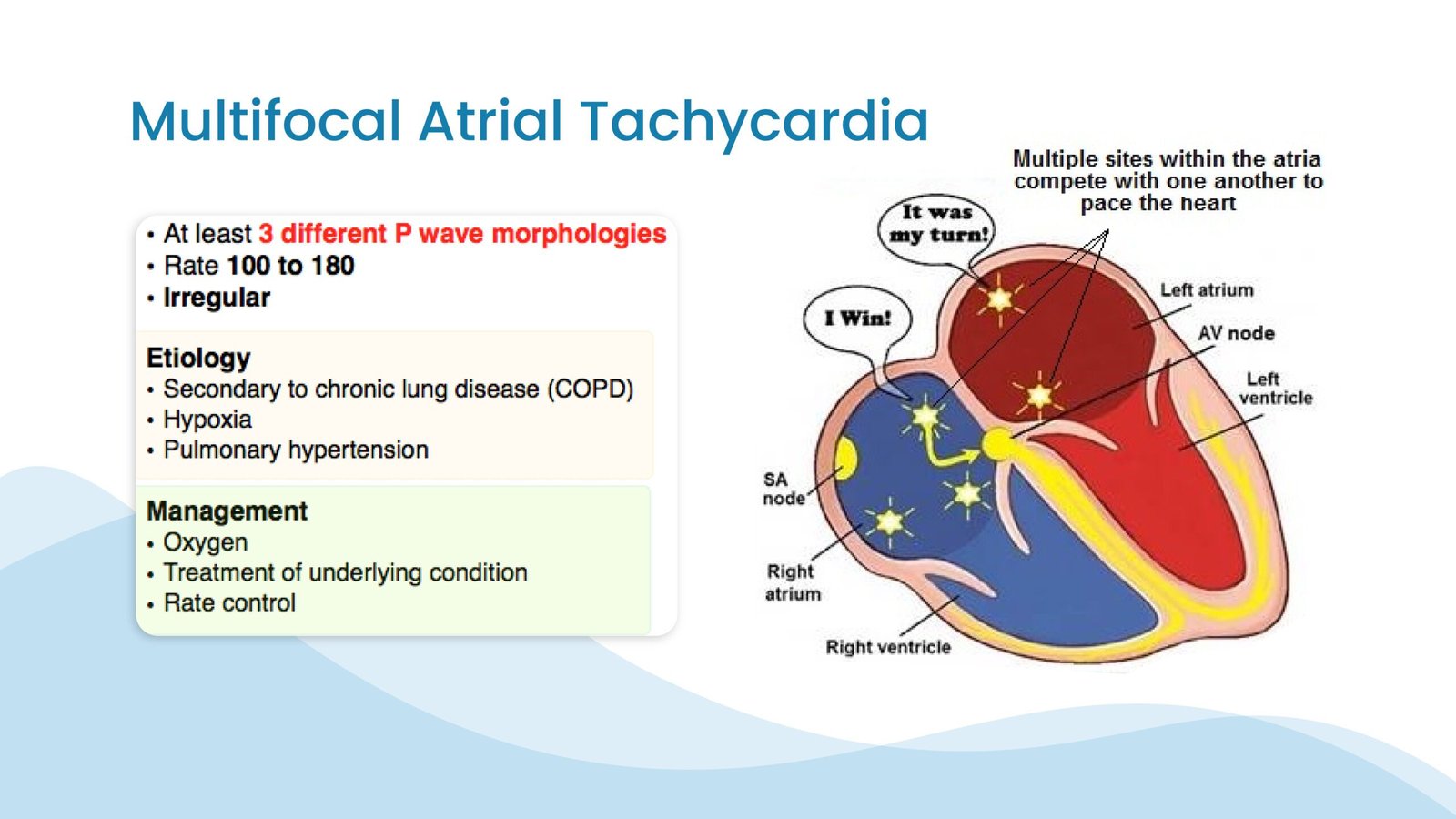
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia is a type of arrhythmia classified by rapid and irregular heartbeats originating from multiple locations in the atria. Atrial Tachycardias originate in the upper chambers of the heart, causing rapid and irregular heartbeats causing abnormal ecg waves. However, more often than not, these heart diseases have a single focal point from where they start in the heart. This distinct characteristic of this heart disease makes it distinguishable from other arrhythmias originating in the atria of the heart.
Normal heartbeats start in a single location, but in the case of MAT, there are various sites from which the electrical signals originate, causing chaos in the heart rhythm. The extensive study of Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia is a fascinating subject that we will cover in this blog. Hence, you can uncover all the key details associated with this arrhythmia through the topics covered below.
What is Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia?
As the name suggests, multifocal atrial tachycardia is an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) starting in the upper chambers, i.e., atria of the heart. Due to having multiple focal centers in the atria, the heart beats chaotically in this heart disease. However, the elevated multifocal atrial tachycardia rate has a rhythmic pattern unlike other tachycardias originating in the atria.
The arrhythmia is often associated with many underlying medical conditions. Some of these conditions include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart failure, or electrolyte imbalances.
The cardiac arrhythmia shares a lot of similarities with atrial fibrillation due to originating in the atria of the heart. However, both arrhythmias differ in their patterns, underlying causes, and treatment approaches. It is crucial to understand the difference between the two arrhythmias for the correct line of approach to treatment and prevention.
multifocal atrial tachycardia vs atrial fibrillation
The following are the differences segregated into the categories of patterns, underlying causes, and treatment approaches for multifocal atrial tachycardia and atrial fibrillation:-
- Origin:
While both arrhythmias originate in the atria of the heart, in atrial fibrillation, the abnormal heart rhythm is due to electrical impulses radiating throughout the atria randomly. At the same time, multifocal atrial tachycardia has rapid and irregular heartbeats originating from multiple locations within the atria. - Rate and Rhythm:
Although both MAT and Afib cause the heart rate to elevate, Afib elevates the heart rate to more than 100 beats per minute with no consistent pattern. On the other hand, the elevated heart rhythm has a more consistent pattern in the case of MAT. - Underlying Causes:
The underlying causes of atrial fibrillation are factors related to age, high blood pressure, heart disease, and thyroid disorders. Whereas, the underlying causes in MAT are medical conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart failure, or electrolyte imbalances. - Treatment Approach:
The treatment approach in the case of Afib is restoring the normal heart rhythm and reducing the risks of blood clots and stroke through medications, cardioversion, or surgical interventions. At the same time, to treat MAT, the underlying medical conditions are identified initially and then the treatment process begins.
How does multifocal atrial tachycardia affect my body?
Multifocal atrial tachycardia can affect the body in numerous ways. Its impact on the body ranges from reduced cardiac output to quality of life impact. Let’s discuss the impact of this heart disease on the body below:-
- Reduced Cardiac Output:
The rapid and irregular heartbeat caused due to MAT can impact the heart’s efficiency in pumping blood to the vital organs of the body. This can potentially result in reduced cardiac output. Due to this conditions like fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath arise. - Decreased Oxygen Delivery:
Due to reduced cardiac output, the oxygenated blood doesn’t reach the vital organs of the body. This causes symptoms like dizziness, lightheadedness, and confusion. - Elevated risk of Complication:
Since MAT is often associated with underlying conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart failure, or electrolyte imbalances, this significantly increases the risk of major cardiac events like strokes. - Decreased Exercise Tolerance:
Reduced cardiac output and decreased oxygen delivery take a heavy toll on exercise tolerance, and the patient tends to get tired too quickly during any physical activity. - Arrhythmia Symptoms:
MAT can potentially cause arrhythmia symptoms like palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, and irregular heart sensations. - Quality of Life Impact:
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia can impact the quality of life through its prominent symptoms. The personal life and work life of the patient tend to get disrupted.
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia causes , Signs and Symptoms
Multifocal atrial tachycardia has many prominent signs and symptoms that indicate the occurrence of heart disease. Multifocal atrial tachycardia is caused by numerous factors. These factors include Underlying Lung Disease, Age, electrolyte imbalances, acute illness or stress, age and coronary artery disease. The following is a list of all these multifocal atrial tachycardia symptoms:-
- Heart Palpitations:
Since the heart rate is elevated in this arrhythmia, the patient experiences heart palpitations, fluttering, and pounding frequently. - Shortness of Breath:
You may face difficulty in breathing, especially when performing a physical activity in this heart condition. - Unexplained Fatigue:
If you are affected by MAT, you might experience unexplained fatigue even with minimal exertion. Chest Discomfort: Some individuals might experience chest pain and discomfort in this arrhythmia. - Dizziness/ Lightheadedness:
Due to reduced blood flow to the brain, you might feel dizzy or lightheaded in this heart disease, especially when you quickly stand up. - Weakness:
You might feel general weakness or unsteadiness in this tachycardia. - Fainting:
If the case of this heart disease is too severe, you might occasionally faint or lose consciousnes
Identification of Risk Factors
Identifying risk factors of multifocal atrial tachycardia is important for early prevention. The risk factors that you can identify in this arrhythmia are as follows:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD):
Respiratory conditions such as COPD which are characterized by chronic inflammation and airflow obstruction in the lungs are identified as one of the risk factors for MAT. Old - Age:
This tachycardia mostly affects people above 65 years. - Underlying Heart Disease:
People with underlying heart diseases such as coronary artery disease, structural abnormalities, and heart failure are likely to be affected by MAT. - Electrolyte Imbalance:
The imbalance of electrolytes such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium can disrupt the electrical activity of the heart and cause MAT. - Acute Illness/ Infection:
Acute illness or infections, especially the ones affecting the respiratory system or causing systemic inflammation can pose a risk factor for multifocal atrial tachycardia. - Hypoxia:
Low oxygen levels in the blood (mostly associated with COPD and sleep apnea) can potentially be a risk factor for MAT. - Hypertension:
High blood pressure affects the electrical signal of the heart and causes arrhythmias like MAT.
- Metabolic Disorders:
Conditions like diabetes or thyroid disorders can have an adverse effect on the heart and metabolism causing multifocal atrial tachycardia.
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Treatment and Diagnosis
Diagnosing multifocal atrial tachycardia is an intricate process and it involves a series of tests that can identify the arrhythmia for further treatment.
- Clinical Assessment:
With the basic clinical assessment, the healthcare professional goes through the medical history of the patient and identifies their heart abnormalities. - Physical Examination:
In the physical examination, the healthcare professional listens to the heartbeats carefully to identify any disruption in the rhythm. - Electrocardiogram:
For vivid insights into the heart’s electrical activity, the Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia ECG test is performed. It gives the details about all the abnormalities associated with the heart through traces of P, Q, R, S, and T waves. - Holter Monitor:
If the MAT is severe, the heart’s electrical activity is monitored for a longer period of time, i.e. 24 to 48 hours using a Holter monitor. - Blood Tests:
Health professionals perform blood tests on the patients to identify the underlying causes of multifocal atrial tachycardia such as electrolyte imbalance. - Imaging Studies:
To assess the heart in-depth, healthcare professionals might perform echocardiography in severe cases of arrhythmias. - Proactive Tests:
In some exceptional cases, healthcare professionals check the response of the patient’s body to physical exertion by performing proactive tests, such as exercise stress testing or pharmacological stress testing.
Preventive Measures and Risk Reduction
You can prevent multifocal atrial tachycardia by early detection of the underlying issues and minimizing the causes that can make the arrhythmia worse. The following steps can be taken as preventive and risk-reduction measures for MAT.
- Manage Underlying Conditions:
Managing the underlying conditions for MAT, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart failure, or electrolyte imbalances is essential for its prevention. - Maintain Electrolyte Balance:
You must maintain the electrolyte balance in the blood by proper diet.
- Monitor Your Medications:
You must ensure the medicines you take do not exacerbate the condition of arrhythmia. For this, consider taking advice from a healthcare professional. - Quit Bad Habits:
If you smoke or drink then quit it right away. - Stay Active and Follow a Healthy Diet:
You must engage in physical activity and consume a highly nutritious diet for the prevention of multifocal atrial tachycardia. - Limit the intake of Stimulants:
You must limit the intake of stimulants like caffeine which could potentially trigger arrhythmias like MAT. - Regular Medical Check-ups:
You must visit a healthcare professional for regular check-ups for the prevention of any kind of arrhythmia.
Is multifocal atrial tachycardia dangerous? Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia is a dangerous arrhythmia with many underlying causes and prominent symptoms. If you identify its symptoms on time, you can easily detect it through various tests, physical examinations, and an ECG. Furthermore, along with medication, you can also prevent it by making some substantial lifestyle alterations. Therefore, timely detection and medical intervention are the keys to getting rid of this heart disease if you are ever affected by it.



