Author:- Mr. Ritesh Sharma
The human heart is covered by a double-walled sac called the pericardial sac. Sometimes, this sac gets filled by a fluid causing a condition called cardiac tamponade. The fluid that gets deposited in the pericardial sac exerts pressure on the heart which dampens its function and leads to the reduction in the cardiac output. There is an increased pressure in the heart in this particular condition causing the heart to work harder than usual. This normally leads to heart palpitations as the cardiac output is reduced.
Cardiac tamponade is a dangerous condition to deal with. However with a steadfast approach towards its management, we can steer clear of this horrifying condition. In this blog, we will examine everything regarding cardiac tamponade. This includes the basic definition, causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention methods. So, get educated by this blog regarding cardiac tamponade and ensure that your heart health stays optimal throughout your lifetime.
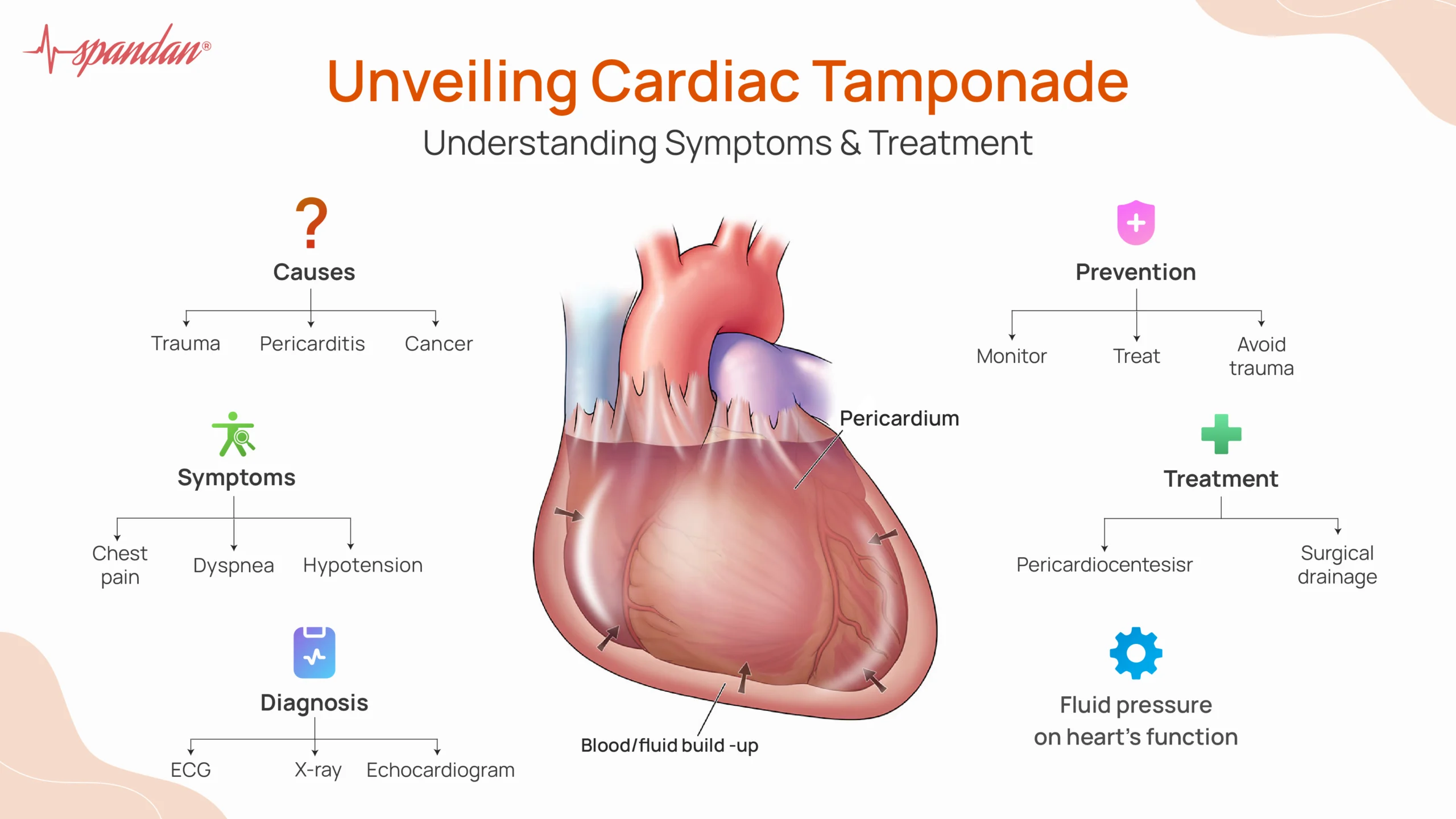
What is Cardiac Tamponade?
Cardiac tamponade occurs when fluid, such as blood or effusion, accumulates rapidly or extensively in the pericardial space, leading to increased pressure on the heart. The heart, compressed by this fluid, struggles to expand and fill properly during diastole, the phase when the heart relaxes and fills with blood. This results in reduced ventricular filling and a subsequent drop in cardiac output, which can quickly become fatal if not addressed.
Cardiac Tamponade Causes
Cardiac Tamponade can be caused by various conditions. Some of these conditions are common while others are uncommon. Let’s discuss these causes one by one below:
- Trauma: Blunt or penetrating chest trauma can cause bleeding into the pericardial space.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the pericardium, often due to infection or autoimmune diseases, can lead to fluid accumulation.
- Malignancy: Cancer, especially lung or breast cancer, can metastasize to the pericardium or cause effusion through obstruction of lymphatic drainage.
- Uremia: Kidney failure can lead to uremic pericarditis and effusion.
- Myocardial Infarction: A heart attack can result in a rupture of the heart muscle, causing blood to leak into the pericardial space.
- Aortic Dissection: A tear in the aorta can lead to blood leaking into the pericardial sac.
Cardiac Tamponade Symptoms
The symptoms of cardiac tamponade can vary depending on the rate and volume of fluid accumulation but typically include:
- Chest Pain: Often sharp and worsening with inspiration or coughing.
- Dyspnea: Shortness of breath, which may be severe and worsen when lying down.
- Tachycardia: An abnormally fast heart rate as the heart attempts to maintain adequate output.
- Hypotension: Low blood pressure due to reduced cardiac output.
- Jugular Venous Distention: Visible bulging of the jugular veins due to increased venous pressure.
- Pulsus Paradoxus: A significant drop in blood pressure during inspiration.
- Muffled Heart Sounds: Heard on auscultation due to the insulating effect of the fluid around the heart.
Cardiac Tamponade Diagnosis
There are numerous ways to diagnose cardiac tamponade. Some of these common diagnostic methods are physical examination, electrocardiogram, X-ray, and echocardiogram. Let’s discuss all these diagnostic methods in detail:
- Physical Examination: Detects signs like hypotension, jugular venous distention, and muffled heart sounds, collectively known as Beck’s triad.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): May show low voltage QRS complexes and electrical alternans (varying QRS amplitude), i.e. QRS complex abnormalities indicative of fluid around the heart.
- Chest X-ray: Can reveal an enlarged cardiac silhouette if the effusion is large.
- Echocardiogram: The gold standard for diagnosing cardiac tamponade, showing fluid accumulation and the collapse of cardiac chambers, especially the right atrium and ventricle during diastole.
Treatment Options
The treatment options for cardiac tamponade include restoring the normal cardiac output which is suppressed by the deposited fluid. For this mostly surgical methods are used by healthcare professionals along with medications:
- Pericardiocentesis: The primary and most urgent intervention, involving the insertion of a needle into the pericardial space to aspirate the excess fluid. This procedure can be guided by echocardiography to ensure accuracy and safety.
- Surgical Drainage: In cases where pericardiocentesis is not sufficient or possible, surgical options such as a pericardial window or pericardiectomy may be necessary. These procedures involve creating a small opening in the pericardium to allow continuous drainage of fluid.
- Treating the Underlying Cause: Addressing the root cause of the tamponade is crucial. For instance, antibiotics for infection, chemotherapy for malignancy, or surgical repair for aortic dissection or myocardial rupture.
- Volume Resuscitation: Administering intravenous fluids can help maintain blood pressure and cardiac output until definitive treatment can be performed.
- Medications: In certain cases, medications like vasopressors may be used to support blood pressure, but they are not a substitute for definitive fluid removal.
Prevention Methods
The prevention methods of cardiac tamponade include timely treatment, regular monitoring, and trauma prevention. With the help of these, you will be able to steer away from the condition and not get affected by it in the slightest:
- Regular Monitoring: Patients with known pericardial effusion or at risk of conditions leading to tamponade should be closely monitored.
- Timely Treatment: Conditions such as infections, malignancies, and inflammatory diseases should be treated promptly to prevent complications like tamponade.
- Trauma Prevention: Using seat belts, helmets, and other protective measures can reduce the risk of chest trauma.
In conclusion, cardiac tamponade is a kind of condition that can pose serious harm to your cardiovascular health if left untreated for a long period of time. While it is a hazardous situation to deal with, if you are affected by it, you must consult a healthcare professional promptly and salvage the situation for yourself. Stay heart-smart and you shall never be harmed by cardiac tamponade or any other heart condition akin to it.



