Author:- Mr. Ritesh Sharma
The human heart consists of many cardiac muscles that work together in a symphony so that blood reaches all vital organs of the body. There are many properties of cardiac muscle that contribute to the function of the human heart. Without these properties of cardiac muscle, the heart would not function so efficiently. The are some key properties of cardiac muscle that are important for optimal heart health.
In this blog, we will decode all the key properties of cardiac muscle, through which it helps maintain optimal cardiovascular health. Understanding these properties is crucial for appreciating how the heart maintains optimal health and how various conditions can impair its performance.
What are the Key Properties of Cardiac Muscle?
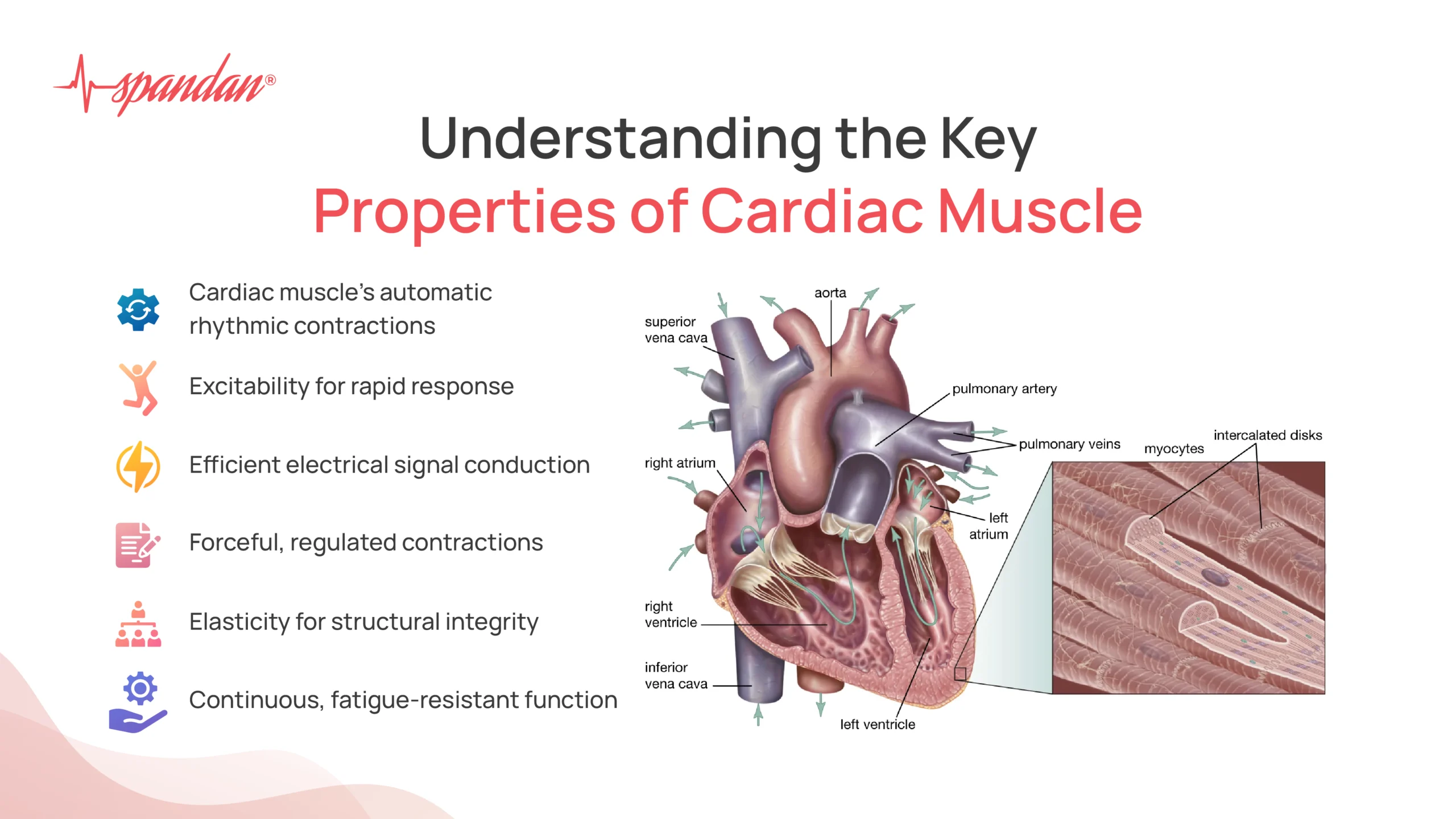
Some of the key properties of cardiac muscle that make it extremely essential for the functioning of the human heart are- automaticity, excitability, conductivity, contractility, elasticity, interconnected structure, metabolic efficiency, and adaptability. We shall discuss each of these properties in a more detailed and refined manner now.
1.) Automaticity
One of the most remarkable features of cardiac muscle is its ability to contract without direct neural stimulation, a property known as automaticity. This intrinsic rhythmicity is primarily driven by pacemaker cells located in the sinoatrial (SA) node i.e. the natural pacemaker of the heart. These specialized cells generate electrical impulses that propagate through the myocardium, initiating and coordinating contractions. Automaticity ensures that the heart maintains a consistent and reliable heartbeat, critical for continuous blood circulation.
2.) Excitability
Excitability refers to the cardiac muscle’s ability to respond to electrical stimuli. When the SA node generates an impulse, it triggers a cascade of electrical activity that spreads across the heart. The cardiac cells possess ion channels that allow for the rapid influx and efflux of ions, leading to the depolarization and repolarization necessary for muscle contraction. This property ensures that the heart can quickly and efficiently respond to each beat, maintaining a steady rhythm and avoiding cardiac arrhythmias.
3.) Conductivity
Conductivity is the property that allows the cardiac muscle to transmit electrical signals rapidly from one cell to another. This is facilitated by the intercalated discs that connect individual cardiac muscle cells. These discs contain gap junctions, which enable the direct passage of ions and electrical impulses between cells. Conductivity ensures synchronized contractions of the heart muscle, which is essential for efficient blood pumping.
4.) Contractility
Contractility refers to the cardiac muscle’s ability to contract forcefully in response to stimulation. This is a vital property for the heart’s function, as it determines the strength of each heartbeat and, consequently, the amount of blood ejected from the heart with each contraction. The contractile force of the myocardium is influenced by several factors, including the availability of calcium ions and the condition of the myocardial tissue. Optimal contractility is crucial for maintaining adequate blood flow to meet the body’s needs.
5.) Elasticity
The elasticity of cardiac muscle allows it to stretch and recoil during the filling and emptying phases of the cardiac cycle. This property is essential for accommodating varying volumes of blood that enter the heart during diastole (relaxation phase) and for ensuring efficient ejection during systole (contraction phase). Healthy cardiac muscle must be both sufficiently elastic to allow for proper filling and resilient enough to contract efficiently.
6.) Interconnected Structure
The cardiac muscle cells are uniquely interconnected by intercalated discs, which are not found in skeletal or smooth muscle. These discs contain desmosomes that provide mechanical strength and gap junctions that facilitate electrical coupling. This interconnected structure ensures that cardiac cells work as a cohesive unit, enhancing the efficiency and coordination of heartbeats.
7.) Metabolic Efficiency
Cardiac muscle has a high metabolic demand and is adapted to generate energy efficiently. It primarily relies on aerobic metabolism and has a rich supply of mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cells, to meet its energy needs. This ensures that the heart has a continuous supply of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), necessary for sustained contractions. The heart’s ability to switch between various energy substrates, such as fatty acids, glucose, and lactate, further underscores its metabolic flexibility and efficiency.
8.) Adaptability
The heart’s ability to adapt to varying demands, such as those imposed by exercise or stress, is another critical property. Cardiac muscle can undergo physiological hypertrophy, where the muscle cells enlarge to increase the heart’s pumping capacity. This adaptability ensures that the heart can meet the increased oxygen and nutrient demands of the body during physical activity or in response to other stressors.
Maintaining Optimal Heart Health
Understanding these key properties of cardiac muscle underscores the importance of maintaining optimal heart health through lifestyle choices and medical interventions when necessary. Here are some strategies to support the health of the cardiac muscle:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular aerobic exercise strengthens the heart muscle, improves its efficiency, and enhances its ability to pump blood. Exercise also promotes the formation of new blood vessels, which can improve blood supply to the heart muscle.
- Balanced Diet: A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports cardiac function. Nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, and antioxidants, found in a variety of plant foods, are particularly beneficial for heart health.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact heart health by increasing blood pressure and heart rate, which can strain the cardiac muscle. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and regular physical activity can help manage stress levels.
- Avoiding Tobacco and Limiting Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can damage the heart muscle and lead to cardiovascular diseases. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake are essential steps in maintaining a healthy heart.
- Regular Health Check-Ups: Routine check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect early signs of heart disease and other conditions that may affect heart health. Monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels can provide important insights into overall cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, the key properties of cardiac muscle that are mentioned in this blog are crucial for their role in maintaining continuous blood circulation and other activities of the heart. Automaticity, excitability, conductivity, contractility, elasticity, interconnected structure, metabolic efficiency, and adaptability are all essential for optimal heart function. By understanding these properties and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, individuals can support the longevity and performance of their heart, ensuring it continues to function optimally throughout their lives.





