Author:- Mr. Ritesh Sharma
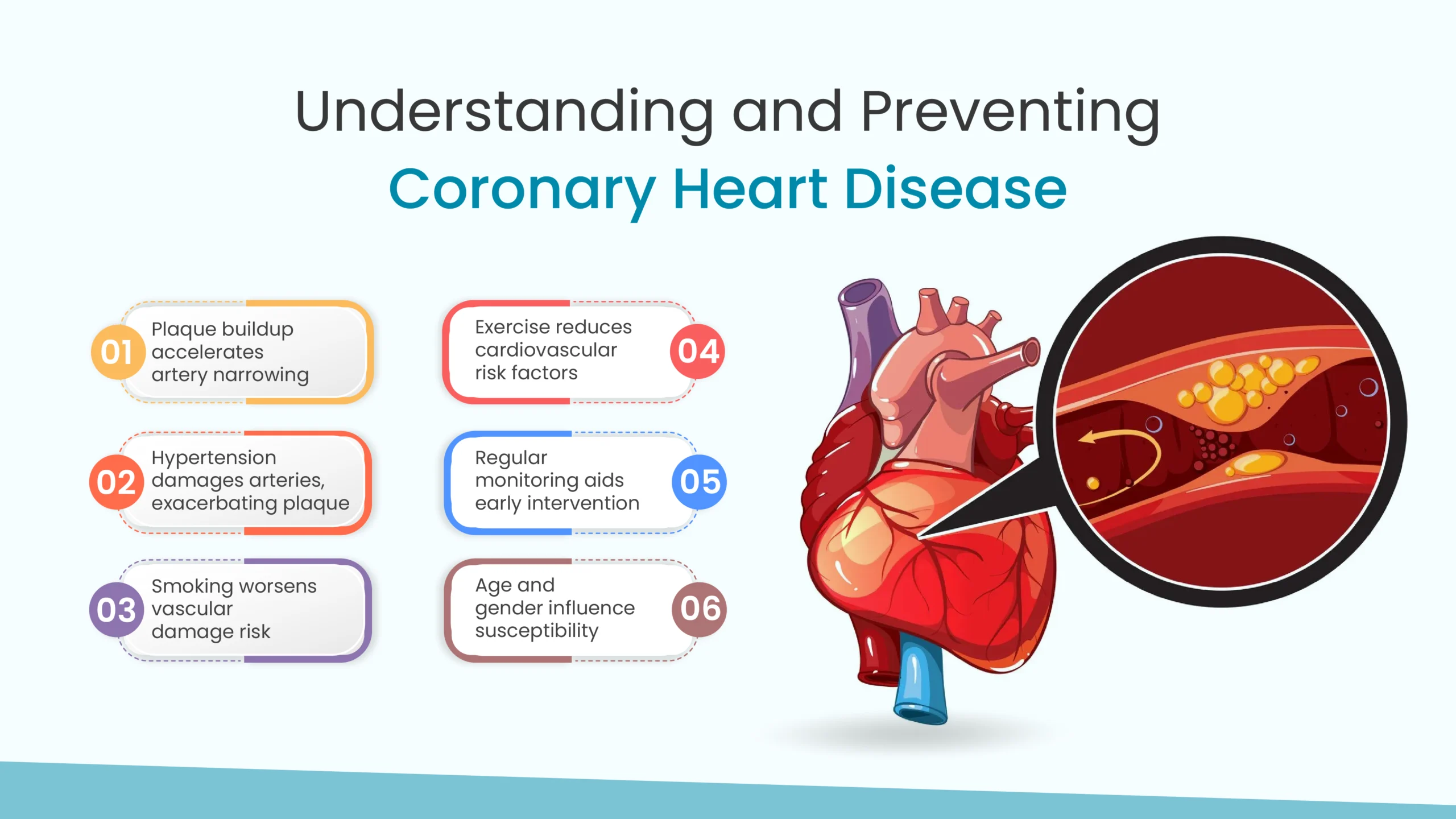
In the realm of cardiac care, coronary heart disease is considered one of the most life-threatening diseases. This disease occurs due to the narrowing down or blocking or coronary arteries (the arteries that are responsible for supplying oxygenated blood to the heart). This narrowing down or blocking of the coronary arteries occurs due to the buildup of plaque in them. Due to this, several complications ranging from chest pain to heart palpitations to something as severe as a heart attack can occur suddenly.
Now, it goes without saying that all of the aforementioned diseases pose a great threat to the human heart. Therefore, understanding and preventing coronary heart disease becomes paramount. We all know that coronary heart disease is severe and if not treated promptly can even turn out to be fatal. However, armed with knowledge about its causes, risk factors, and preventive measures, we can take proactive steps to mitigate its impact on our lives.
In this blog, we will make an attempt to understand the prevention of coronary heart disease. For this, we will cover its basic definition, symptoms, causes, diagnostic methods, preventive measures, and more. So, whether you are a part of a general audience or clinicians, you will be empowered and educated by this blog.
Understanding Coronary Heart Disease
Causes and Mechanisms:
CHD typically develops over time and is often the result of a combination of factors, including:
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of plaque in the arterial walls.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can damage the arteries, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL (“bad”) cholesterol can contribute to plaque formation.
- Smoking: Tobacco use damages blood vessels and accelerates atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of CHD.
Symptoms:
Recognizing the symptoms of CHD is crucial for early detection and intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Pain, numbness, or tingling in the arms or shoulders
- Fatigue
- Indigestion or heartburn
Diagnosis:
Healthcare professionals use various tests to diagnose CHD, including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Through an abnormal ECG showcasing t-wave abnormalities, such as ST-elevation or ST-depression, we can find out the occurrence of coronary heart disease.
- Stress tests: These tests evaluate the heart’s response to physical exertion, helping diagnose CHD by detecting abnormal changes in blood flow during exercise.
- Echocardiography: Ultrasound imaging of the heart can assess cardiac structure and function, detecting any abnormalities associated with CHD.
- Coronary angiography: Considered the gold standard for diagnosing CHD, coronary angiography involves the injection of contrast dye into the coronary arteries followed by X-ray imaging to visualize any blockages or narrowing.
Preventing Coronary Heart Disease
For the prevention of coronary heart disease, it is important to adopt a steadfast approach. You must eat well, exercise enough, quit bad habits, and manage stress. This might appear daunting on listening. However, it is worth it for the prevention of coronary heart disease which has been affecting people worldwide in great numbers. The following is a list of the detailed prevention methods for coronary heart disease.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
- Balanced Diet: Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for CHD, so strive to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, seek support and resources to quit. Even secondhand smoke can increase the risk of CHD.
Manage Chronic Conditions:
- Control Blood Pressure: Monitor your blood pressure regularly and take prescribed medications as directed.
- Manage Cholesterol Levels: Work with your healthcare provider to monitor and control your cholesterol levels through lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medication.
- Control Diabetes: Keep your blood sugar levels within target range through diet, exercise, medication, and regular monitoring.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to the development of CHD. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or hobbies that you enjoy.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure and contribute to weight gain. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation (no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men).
- Regular Health Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your overall health and assess your risk factors for CHD. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Identifying Risk Factors
Recognizing the risk factors associated with CHD is paramount for early intervention and prevention. These risk factors can be broadly categorized as modifiable and non-modifiable:
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: These include age, gender (men are at a higher risk until women reach menopause), family history of CHD, and genetic predisposition.
- Modifiable Risk Factors: These encompass lifestyle choices such as smoking, poor diet, physical inactivity, obesity, hypertension, and diabetes. Addressing these modifiable risk factors through lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the risk of developing CHD.
In conclusion, coronary heart disease is one of the deadliest heart diseases out there. However, with a positive approach to diet, exercise, and other aspects of lifestyle, you can definitely prevent it. In case you are still affected by coronary heart disease, you must not fret and must consult a healthcare professional promptly. Depending on the type and severity of the coronary heart disease, the healthcare professional would suggest a treatment plan, and with a positive attitude and adherence to all instructions provided by the healthcare professional, you will be able to beat the disease effectively.



