Author:- Mr. Ritesh Sharma
Myocardial Infarction is commonly referred to as a heart attack. As soon as you hear about this horrifying medical condition, you think of something life-threatening. You are not wrong to think that. However, heart attacks can be cured if they are detected timely through MI ECG. An electrocardiogram through an ECG machine detects a heart attack promptly and you can opt for treatment immediately. So, if you or your loved one encounters a heart attack, you must consult a healthcare professional and get their MI ECG done.
The MI ECG does not only tell you about the presence of a heart attack but also conveys details about its severity. Through this blog, we aim to provide a comprehensive guide on how ECGs are used to detect myocardial infarctions, explaining the basics of ECG interpretation, common patterns seen in MI, and the importance of early detection.
What is an ECG (Electrocardiogram)?
An electrocardiogram or an ECG is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time. It is performed using electrodes placed on the skin of the chest, arms, and legs. The ECG captures the heart’s electrical impulses and displays them as a series of waves on a graph, which can then be analyzed by healthcare professionals.
Understanding the Basics of ECG
Before diving into the specifics of MI ECG, it is essential to understand the basic components of an ECG. The ECG waveform consists of several key parts:
- P Wave: Represents atrial depolarization, which is the electrical activity associated with the contraction of the atria (the upper chambers of the heart). An abnormal ECG showcases P-wave ECG abnormalities in the ECG waveform pattern.
- QRS Complex: Represents ventricular depolarization, the electrical activity related to the contraction of the ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart). This complex consists of the Q wave, R wave, and S wave. An abnormal ECG showcases QRS ECG abnormalities in the ECG waveform pattern.
- T Wave: Represents ventricular repolarization, which is the process of the ventricles recharging electrically in preparation for the next contraction. An abnormal ECG showcases T-wave ECG abnormalities in the ECG waveform pattern.
- ST Segment: The flat section of the ECG between the end of the S wave and the start of the T wave. It is crucial in MI detection.
How MI Affects the Heart?
A myocardial infarction occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked, usually due to a blood clot in one of the coronary arteries. This blockage causes ischemia (reduced blood flow), which can lead to damage or death of the heart tissue if not promptly treated. The ECG changes associated with MI are due to the effects of ischemia, injury, and infarction on the heart’s electrical activity.
What is MI ECG?
ECG changes during an MI can vary depending on the severity and location of the infarction. The following are the most common patterns seen in the ECG of a patient experiencing an MI:
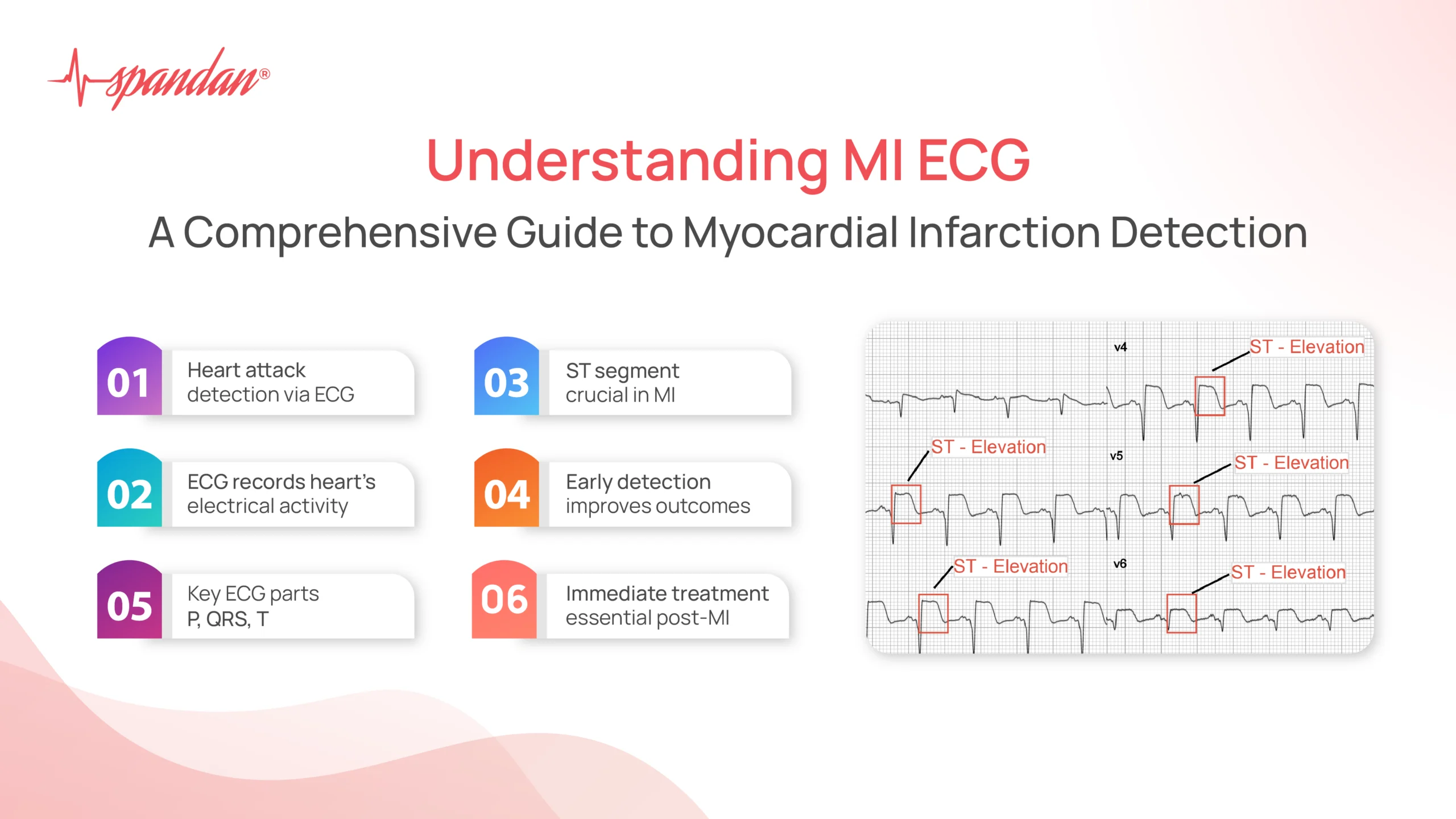
ST Elevation
ST Segment Elevation: One of the hallmark signs of an acute MI is ST segment elevation. This elevation indicates that a portion of the heart muscle is undergoing severe ischemia and injury. The specific leads showing ST elevation can help localize the area of the heart affected:
- Inferior MI: ST elevation in leads II, III, and aVF.
- Anterior MI: ST elevation in leads V1 to V4.
- Lateral MI: ST elevation in leads I, aVL, V5, and V6.
- Posterior MI: ST depression in leads V1 to V3 (indicative of posterior involvement).
Pathological Q Waves
Q Waves: The development of pathological Q waves (wider and deeper than normal) on the ECG suggests that there has been significant myocardial damage, leading to a loss of electrical activity in the affected area. This usually indicates a more extensive infarction.
T Wave Inversion
T Wave Changes: T wave inversion or flattening can also indicate myocardial ischemia. These changes often follow ST segment elevation and can persist for days to weeks after the acute event.
ST Depression
ST Segment Depression: While ST segment elevation is typically associated with acute MI, ST depression can also occur, particularly in the setting of non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) or ischemia in areas of the heart not directly involved in the infarction.
The Importance of Early Detection in MI ECG
Early detection and treatment of MI are crucial for improving patient outcomes. Prompt diagnosis allows for timely intervention, which can minimize heart muscle damage and reduce the risk of complications. ECG is a cornerstone of MI diagnosis due to its ability to quickly and non-invasively provide critical information about the heart’s condition.
Initial Steps in ECG Interpretation for MI
- Assess Patient Symptoms: Correlate ECG findings with the patient’s symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and other signs of a heart attack.
- Identify ST Segment Changes: Look for any ST segment elevation or depression, as these are key indicators of myocardial ischemia or injury.
- Evaluate Q Waves: Check for the presence of pathological Q waves, which suggest myocardial necrosis.
- Analyze T Waves: Observe any changes in T waves, such as inversion or flattening, which can indicate ongoing ischemia.
Advanced ECG Interpretation
Interpreting an ECG for MI requires not only identifying obvious changes but also understanding subtler patterns and variations. Clinicians often use additional criteria and tools, such as:
- Serial ECGs: Comparing multiple ECGs over time to observe the evolution of changes.
- Reciprocal Changes: Identifying opposite changes in leads that view the heart from different angles, which can support the diagnosis.
- Clinical Context: Integrating ECG findings with clinical history, physical examination, and other diagnostic tests, such as cardiac biomarkers (e.g., troponin levels).
Treatment Following MI Detection
Once an MI is detected via ECG, immediate treatment is essential. Treatment strategies may include:
- Medications: Such as antiplatelet agents (aspirin), anticoagulants (heparin), nitrates, beta-blockers, and thrombolytics to dissolve clots.
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): Also known as angioplasty, this procedure involves mechanically opening the blocked artery using a balloon and often placing a stent to keep it open.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): A surgical option for severe cases, where a blood vessel from another part of the body is used to bypass the blocked artery.
In conclusion, MI ECG is crucial in detecting one of the most hazardous heart conditions in the domain of cardiac care. The ECG provides invaluable information that, when combined with clinical assessment and other diagnostic tools, allows for rapid and accurate diagnosis of MI. Early detection and treatment significantly improve patient outcomes, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing recovery. By recognizing the key ECG changes associated with MI, clinicians can promptly initiate life-saving interventions and provide the best possible care for patients experiencing a heart attack.




